Refers to the Instantaneous Rate of Change of Profit
Y 3x 2 2x. An average rate of change tells you the average rate at which something was changing over a longer time period.
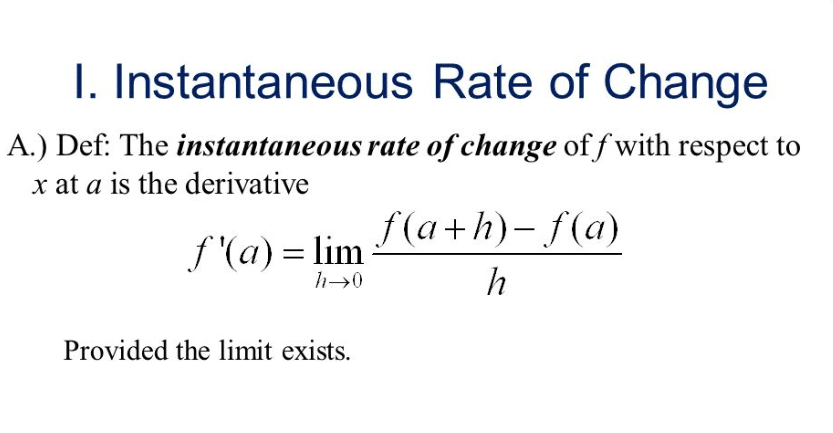
Average And Instantaneous Rate Of Change The Education
B Find the instantaneous rate of change of Cwith respect to xwhen x 100 Marginal cost when x 100 usually explained as the cost of producing an extra unit when your production level is 100.
. 6 2 2. Refers to the comparison of the instantaneous rate of change of an economic variables. When we think about a rate of change as representing a slope our existing strategies require knowing two different points to compute a slope.
When we project a ball upwards its position changes admin September 18 2019. The instantaneous rate of change of profit with respect to the number of items sold. Find P 325 P 325 the rate of change of profit when the price is 325 325 and decide whether or not the coffee shop should consider raising or lowering its prices on scones.
Instantaneous rate of change rate of change at a given instant in time Rate of change technical analysis a simple technical indicator in finance See also Rate of climb or rate of altitude change in aeronautics Rate disambiguation Change disambiguation Frequency disambiguation Gradient disambiguation. Known Function y f x 5x 3 4x 2 2x 1. Thus the instantaneous rate of change at x 2.
Limdeltax-0 deltay deltax limdeltax-0 fxdeltax - fx deltax if y is a distance and x is time then the rate of change is a velocity. Solution The instantaneous rate of change of Cwhen x 100 It is given by lim x100 x y lim x100 fx f100 x 100 lim x100 50 p x 50 p 100 x 100 lim x100 p x 10. Unless we use the phrase Average Rate of Rhange we will assume that in calculus the phrase Rate of Change refers to the Instantaneous Rate of Change.
Some of the entries in Column 2 do not apply Aline that touches a curve at a point without crossing over Choose A line which passes through at least two points of a curve Choose The change in the y-value divided by the change in the x-value for two distinct points on the graph Choose The rate of change of a function occurring as a limit approaches zero Choose The. Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change Instantaneous Rate Of Change. If x is the number of units of a product produced in some time interval then C xis the total cost of producing x items C x 1is the cost of producing x 1 items.
Margin refers to an instantaneous rate of change that is a derivative. The instantaneous rate of change or simply rate of change of y fx as x is the limit of the average rate of change on the interval x xx as x approaches 0 Velocity If y is a distance and x is time then the rate of change velocity. Find the instantaneous rate of change for the function y 3x 2 2x at x 2.
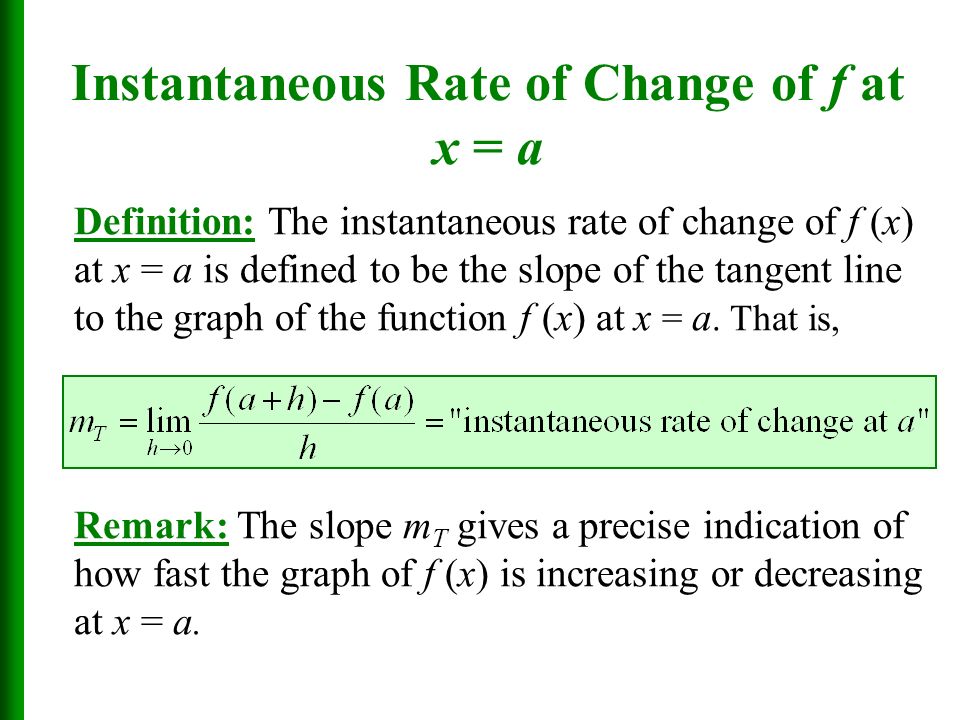
Find and interpret the instantaneous rate of change of profit with respect to the number of items produced when x2. F 2 46. We have already seen that the instantaneous rate of change at a point is the same as the slope of the tangent line at a point aka the derivative at that point.
The instantaneous rate of change of a function is the rate of change at a particular point. Suppose that the total profit in hundreds of dollars from selling x items is given by. Refers to the total revenue from the sale of x units of a product or service.
Refers to the mass of an object per unit length. In business the total cost to produce x units do a product or service. From now on unless we use the phrase average rate of change we will assume that in calculus the phrase rate of change refers to the instantaneous rate of change.
Refers to the instantaneous rate of change of total profit with respect to the number of items sold demand function or price function is px where p is the number of units of a product or service that can be sold at a particular price x. The coffee shop currently charges 325 325 per scone. F x 5 3x 2 4 2x 2 0.
P 325 20 0 P 325 20 0. The derivative of a constant function is the zero function. When x 2 it becomes.
Thus if Cx is the total cost of producing x items then is called the marginal cost and represents the instantaneous rate of change of total cost with respect to the number of items produced. We see changes around us everywhere. Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change Instantaneous Rate Of Change.
Then the exact costof producing the x 1stitem is C x 1 C x The marginal costis C x 4 Example 1. The instantaneous rate of change is. Refers to the total revenue from the sale of x units of a product or service.
The instantaneous rate of change of total profit with respect to the number of items sold. Instantaneous Rates of Change We have already seen that the instantaneous rate of change is the same as the slope of the tangent line and thus the derivative at that point. We see changes around us everywhere.
When we project a ball upwards its position changes. While you were on your way to the grocery store your speed was constantly changing. Stay tuned with BYJUS for more such interesting articles.
In business the total cost Cx to produce x units of a product or service. The instantaneous rate of change or simply rate of change of y fx at x is the limit of the average rate of change on the interval x x deltax as deltax approaches 0. In economics the word marginal refers to a rate of change that is to a derivative.
Refers to the instantaneous rate of change of profit Other questions on the subject. When you measure a rate of change at a specific instant in time this is called an instantaneous rate of change. F x 15x 2 8x 2.
F 2 15 2 2 8 2 2 60 16 2 46. Hence the instantaneous rate of change is 10 for the given function when x2. We expect that the average rate of change between two points should approximate the instantaneous rate of change if the increment Delta x is not.
Thinking logically through this formula we are finding the difference. Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change. Biology 22062019 0600.
The average rate of change and the slope of a line are the same thing.

Differentiation Purpose To Determine Instantaneous Rate Of Change Eg Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Total Cost Per Unit Of The Good We Will Learn Marginal Ppt Download

Solved Estimate The Instantaneous Rate Of Change Of The Chegg Com

Chapter 3 Introduction To The Derivative Sections 3 5 3 6 4 Ppt Video Online Download
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Refers to the Instantaneous Rate of Change of Profit"
Posting Komentar